Modification of “one number” service
We upgraded miniSIPServer V30 today to change “one number, multi-devices” service in local user’s configuration. In previous versions, we don’t need configure anything to enable this feature in local user since it was enabled by default. Customers think it is good idea to reduce configuraiton workload, but it brings new management problem. In fact, they hope to be able to control which local users can have this feature. In most scenarios, only some local users have several phones with same number, others are not permit to do that.
To fit this requirement, we add a new optional item in local user’s configuration. Please refer to following figure for more details. By default, this service is not enabled now until you configure it obviously.
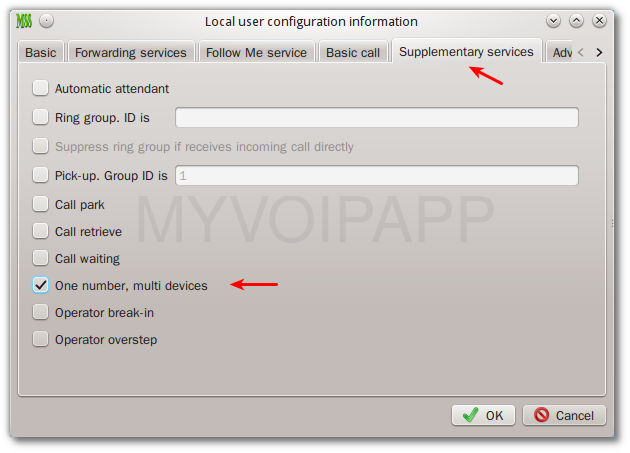
This modification is applied to cloud MSS too.