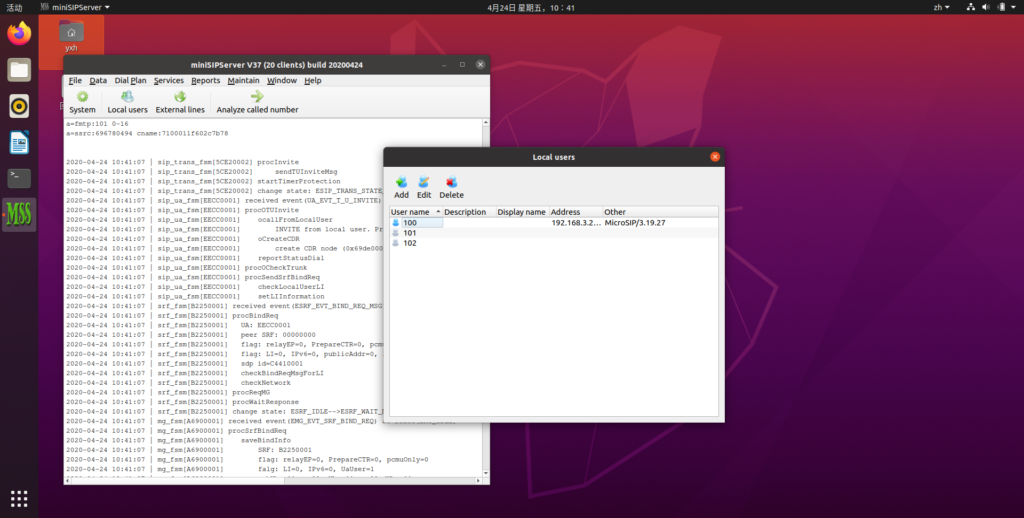
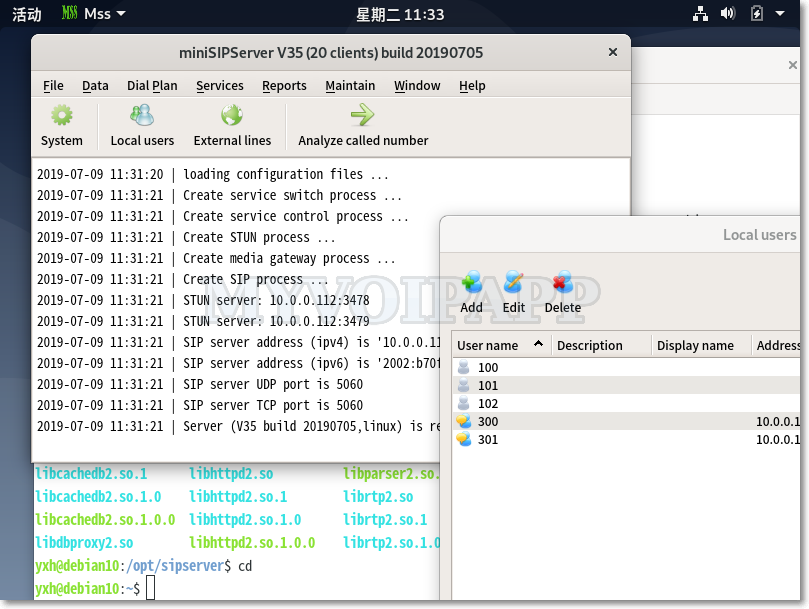
Refined ringing group
In normal, we configure ringing group information in local users’ profile. And one user can only be assigned to one ringing group. It works in most scenarios.
As you know, it is hard time now. Some companies reduce their human resources to save cost, so someone has to take more works. For example, it is possible that someone could be assigned to several ringing groups at the same time. In fact, some customers have requested us to fit this requirement.
We understand that completely, so miniSIPServer is upgraded to have a new method to provide ringing group service.
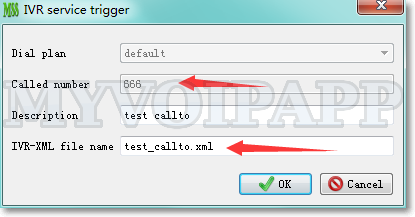
Two independent tables are added. One is used to define ringing groups and their users. Please refer to below figure.
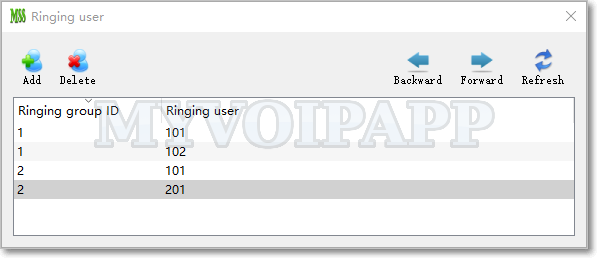
Another table is used to detect ringing groups according to called numbers in different calls. Please refer to below figure.
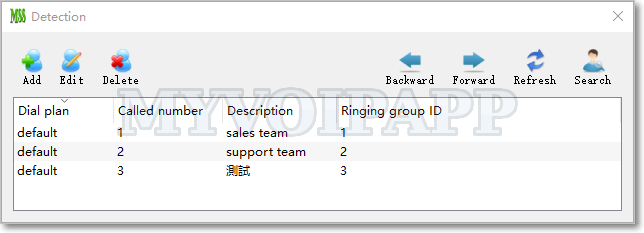
Service document has been updated. Please click here to get more details about this new feature.